Content

Food and Drug Administration for use in treating nicotine or tobacco dependence. COGS excludes indirect costs such as overhead and sales & marketing. This means that companies sometimes spend slightly more or less money on production than was expected. However, this knowledge can be used to budget better in the future to understand the causes of these differences and aim to reduce costs.
- For example, if the COGM reveals that the overheads are the main reason for the losses, the company may be able to cover the loss by producing more of the product.
- If a company can reduce its COGS through better deals with suppliers or through more efficiency in the production process, it can be more profitable.
- It excludes indirect expenses, such as distribution costs and sales force costs.
- If the inventory value included in COGS is relatively high, then this will place downward pressure on the company’s gross profit.
- The two most important numbers on this statement are the total manufacturing cost and the cost of goods manufactured.
- The resulting figure will include the cost of any scrap or other direct materials shrinkage that may have occurred during the period.
Study the definition of cost of goods and how to calculate it in this lesson. The cost of goods manufactured appears in the cost of goods sold section of the income statement. The cost of goods manufactured is in the same place that purchases would be presented on a merchandiser’s income statement. We add cost of goods manufactured to beginning finished goods inventory to derive cost of goods available for sale. This is similar to the merchandiser who presents purchases added to beginning merchandise to derive goods available for sale. More items were sold than produced during the accounting period (i.e. some items were sold from the last period’s remaining finished goods inventory). The company employs eight shop floor workers that are directly responsible for the execution of production processes.
How do you calculate the cost of goods manufactured?
All of the above will also allow the firm to properly plan its resource utilization, product pricing strategy, volume production planning, etc. Further, this statement will also serve as the basis for the comparison of operations of manufacturing on a year-to-year basis. It shall help in setting out with appropriate classification of the elements of the costs in detail. Hence, the cost of goods manufactured will be 13,66,47,400 and per unit, it will be 1,366,474 when divide it by 100. According to these basic calculations, the quarterly COGM of the furniture company is 97,200 dollars.
- In spite of the similarities in the names, the cost of goods manufactured is not interchangeable with the cost of goods sold .
- The cost of goods sold is therefore zero, while the cost of goods manufactured may be substantial.
- During periods of rising prices, goods with higher costs are sold first, leading to a higher COGS amount.
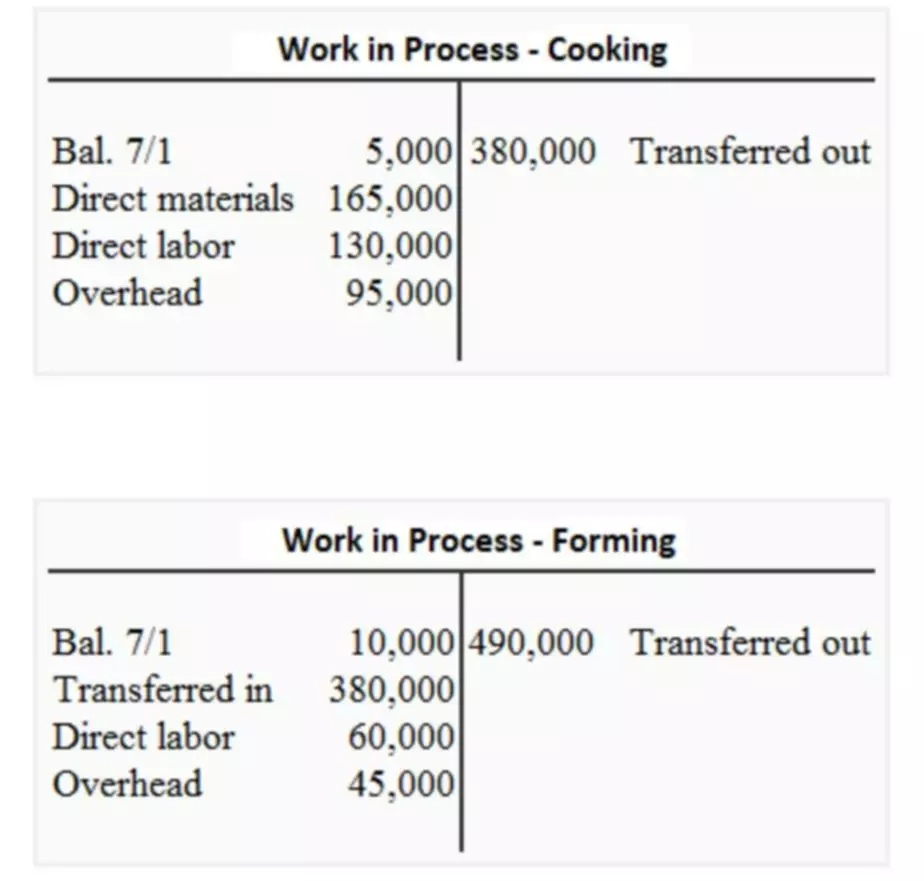
- The sum of all amounts transferred from the Work in Process account and into the Finished Goods account represents the Cost of Goods Manufactured for the period.
- By doing so, you can determine the types of costs that a company is incurring over time to produce a certain mix and quantity of goods.
- Once all of this is ready, it’s time to put together a complete schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured and Cost of Goods Sold.
There may be no sales at all during the period, while production has continued. The cost of goods sold is therefore zero, while the cost of goods manufactured may be substantial. Thus, the total cost of goods manufactured for the period would be $265,000 ($100,000 + $50,000 + $125,000 + $65,000 – $75,000). This means that Steelcase was able to finish $265,000 worth of furniture during the period and move this merchandise from the work in process account to the finished goods account by the end of the period. If you’re wondering where you can find the cost of good manufactured, take a look at the cost of goods sold section on the income statement. COGM is a key component of computing the cost of goods sold .
AccountingTools
Knowing the cost of goods sold helps analysts, investors, and managers estimate the company’s bottom line. While this movement is beneficial for income tax purposes, the business will https://www.bookstime.com/ have less profit for its shareholders. Businesses thus try to keep their COGS low so that net profits will be higher. A company’s COGM is strongly tied to its cost of goods sold .

Next, you add in all raw materials purchased during that same period. However, COGM is part of the COGS formula in periodic inventory accounting. COGM is assigned to units in production and is inclusive of WIP and finished goods not yet sold, whereas COGS is only recognized when the inventory in question is actually sold to a customer. Before we delve into the COGM formula, reference the formula below that calculates a company’s end-of-period work in progress balance.
Understanding Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
To speak to an expert about how to automate your accounting, request a quick demonstration of ScaleFactor’s accounting and finance software here. Then, the value for the Cost of Goods Manufactured is transferred to the account for the final inventory named the Finished Goods Inventory account, where it is used to compute the Cost of Goods Sold. After all the necessary figures are computed that need to be used to calculate the Cost of Goods Manufactured for a year, the Cost of Goods Manufactured is calculated and then placed in the Finished Goods Inventory account. Usually, timesheets and time logs are used, and the business takes the total number of hours the employees worked and multiplies these by the hourly wage rate.
After using the equivalent units of production calculation, the Steelcase managers were able to determine that the ending goods in process inventory was $75,000. Finished Goods Inventory, as the name suggests, contains any products, goods, or services that are fully ready to be delivered to customers in final form. The following T-account shows the Finished Goods Inventory. Beginning and ending balances must also be considered, similar to Raw materials and WIP Inventory. In the debit side of the raw materials inventory T-Account.
Linking COGM to COGS
Beginning and ending balances must also be used to determine the amount of direct materials used. The total labor and all manufacturing costs other than direct labor are known as conversion costs. These include indirect labor, quality control inspection, indirect materials, machine setups, factory supervision etc.
In theory, COGS should include the cost of all inventory that was sold during the accounting period. In practice, however, companies often don’t know exactly which units of inventory were sold. Instead, they rely on accounting methods such as the first in, first out and last in, first out rules to estimate what value of inventory was actually sold in the period. If the inventory value included in COGS is relatively high, then this will place downward pressure on the company’s gross profit. For this reason, companies sometimes choose accounting methods that will produce a lower COGS figure, in an attempt to boost their reported profitability. The Cost of Goods Manufactured is a statement that shows the total cost of producing products for a company during a specific period.
The final number derived from the calculation is the cost of goods sold for the year. COGS differs from operating expenses in that OPEX includes expenditures that are not directly tied to the production of goods or services. Cost of goods sold includes all of the costs and expenses directly related to the production of goods. COGM is important because it helps determine the net income a company can generate from its production process or changes required to make it profitable.



