Content

An investment with fixed-payments that occur at regular intervals, paid at the end of each period. The essential thing to understand about ordinary annuities is that the payments are made at the end of the intervals periods rather than at the beginning. An ordinary annuity is an annuity which makes its payment at the end of each interval period.
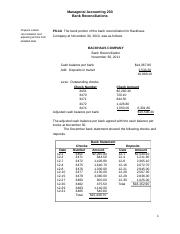
Since all payments are in the same amount ($80), they are made at regular intervals , and the payments are made at the end of each period, the coupon payments are an ordinary annuity. When interest rates rise, the value of an ordinary annuity is reduced.
AccountingTools
In just a few minutes, you’ll have a quote that reflects the impact of https://personal-accounting.org/, interest rates and market value. The first payment is received at the start of the first period and, thereafter, at the start of each subsequent period. Let’s look at a few examples to better understand the concept of ordinary annuities. Another notable difference between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due is how it is valued.
However, if a month passes before you make your first monthly payment on the loan, your original principal accumulates more interest than if the principal had already been reduced. This is called making your payment at the end of the payment interval, and this payment is known as an ordinary because it is the most common form of annuity payment. Depending on when you make your payment, different principal and interest amounts occur.
Amortization calculations
The 401k Ordinary Annuity Definition lets you assess the final balance in your 401k savings account and how long the annuity will last. Interest rate is the annual nominal interest rate expressed as a percentage. Since compounding frequency is 1, set Number of Compounding Periods (C/Y) to 1by pressing [P/Y]. Get personal finance tips, expert advice and trending money topics in our free weekly newsletter. Learning the true market value of your annuity begins with recognizing that secondary market buyers use a combination of variables unique to each customer. Kim Borwick is a writer and editor who studies financial literacy and retirement annuities.
